Every year or two, Intel launches its newer generation of processors in the market. Some of them are already compatible with older motherboard sockets whereas others require a completely new motherboard to fit in. This is because some processors are only compatible with the specific socket they are designed for. Intel commonly identifies the motherboard socket by the “LGA” prefix. The last two generations of CPUs either fit in LGA 1200 or LGA 1700 sockets. So there’s confusion among PC builders and enthusiasts regarding which one to go with.
To know which one suits your taste, it is important to know about the main differences between these two sockets. And this guide we will list out the features and capabilities of these two sockets to give you an idea of which one is better for your needs.
Contents
What are LGA 1200 and LGA 1700 sockets?
We’ll start with the LGA 1200 chipset first which was first launched by Intel in 2020. The LGA 1200 served as the base for mounting Intel’s Comet Lake (10th-gen) and Tiger lake (11th-gen) processors.
Compared to the previous generation sockets, the LGA 1200 showed a massive improvement in power efficiency and faster memory support. Additionally, the LGA 1200 socket was smaller in size as compared to previous sockets, resulting in better thermals and easier installation.
LGA 1700 chipset on the other hand was launched in 2021 and is the most recent socket used for running next-generation CPUs in Intel’s 12th and 13th generation line-up. The LGA 1700 socket comes up with improved performance over the LGA 1200 socket, which we’ll discuss later on in this guide.
LGA 1200 vs LGA 1700: Explained
So here’s a brief summary of what you’ll find out in this guide. We’ll start with the main definitions of both socket types and then we’ll move on to the features, compatibility, performance, overclocking potential, and finally the conclusion part.
Features
When it comes to features, there are a lot of stories to be told at this point. From LGA 1200 to LGA 1700, everything has totally changed in terms of the number of pins, size of the socket, design, and other details.
Number of Pins
One of the major differences between the LGA 1200 and LGA 1700 sockets is the number of pins. The LGA 1200 socket only had 1200 pins, whereas, in Intel 1700 socket, there are a total of 1700 pins to make contact with the pads on the CPU. This results in a more stable connection between the processor and motherboard, hence improving the performance.
Socket Size
Although, the LGA 1200 socket is smaller in size, but makes use of the same square shape that most previous sockets do. LGA 1200 has a width of 37.5 mm and a length of 37.5 mm, while LGA 1700 has a width of 37.5 mm and a length of 45.0 mm.
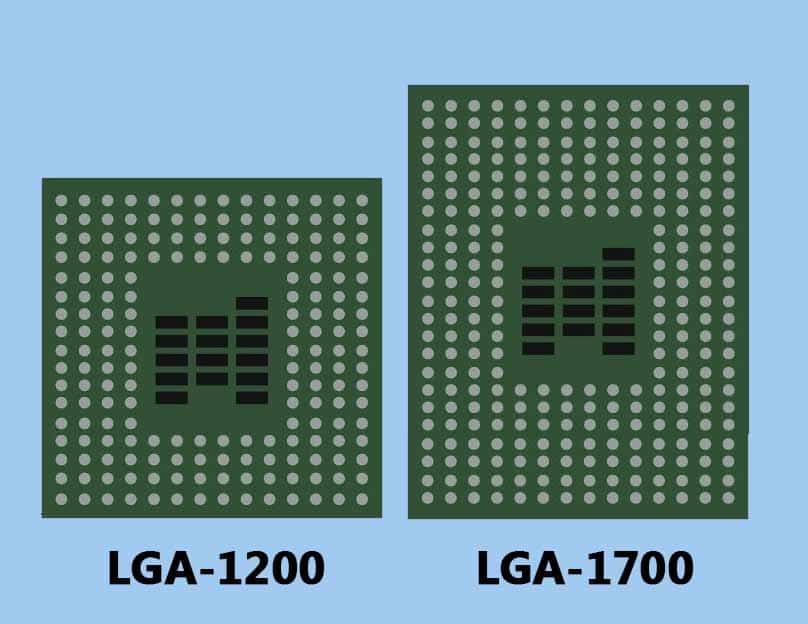
Therefore, the LGA 1200 socket is now 7.5mm longer in length as compared to the LGA 1200 socket. This additional length on the LGA 1700 socket makes it look rectangular in shape rather than square.
The change in socket size also changes the cooling requirement of the LGA 1700 socket. You’ll now need a relevant CPU cooler for LGA 1700-compatible CPUs. So when choosing a CPU cooler for an LGA 1700 compatible motherboard, you’ll have to make sure that it easily fits in the said socket.
But for LGA 1200 socket CPUs, you don’t need to be too picky to choose a CPU cooler. The LGA 1200 supports a wide range of CPU coolers on the market as compared to the LGA 1700 socket.
Power delivery
Both the LGA 1200 and LGA 1700 show improved power delivery performance over the previous sockets. But when you put both of them side by side, then there’s a significant power delivery system difference among both sockets.
LGA 1200 socket offers 14 power phases to support both the low and high-performance CPU. The LGA 1700 on other hand takes you a step further depending on the type of motherboard that you have. For example, a motherboard like ASUS Z790 supports 20+1 phases for extreme performance.
Memory support
In terms of memory support, the LGA 1200 falls behind the LGA 1700 socket. With LGA 1200, you are limited to DDR4 memory modules whereas the LGA 1700 offers support for both DDR4 and DDR5 high-speed memory.
Having support for both memory types makes the LGA 1700 socket motherboards a more reasonable choice for PC enthusiasts.
Socket key mechanism
The role of the socket key mechanism is to ensure that the processor sits properly on the socket once you install it. It consists of a small key that is attached to the socket and corresponds to the bottom notch of the CPU.
When the CPU is placed on the socket, the notch present on the socket sticks into the key, thus locking the CPU to the motherboard socket. This helps in providing a firm connection between your processor and motherboard.
The socket key mechanism in LGA 1700 socket uses 4 keys which is different from that of the LGA 1200 socket which uses 2 keys.
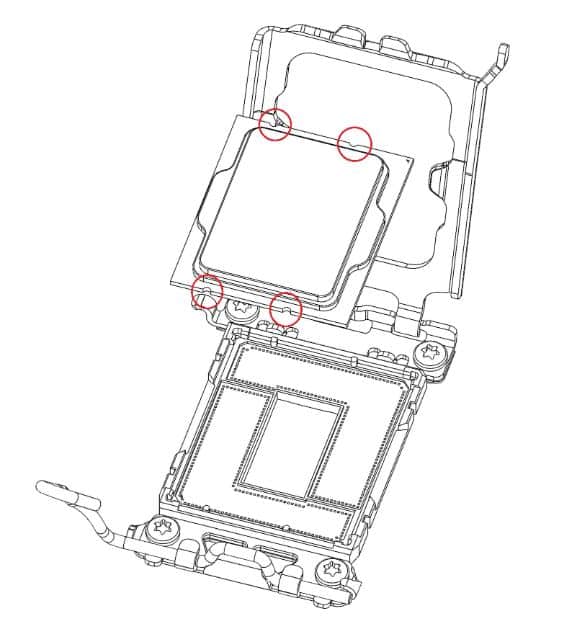
The different socket key mechanism also leads to different pin indicator on both sockets. So you have to closely look out for the pin indicator when installing LGA 1700 or LGA 1200 compatible CPU.
Compatibility
We’ll divide the compatibility into two parts, CPU compatibility and motherboard compatibility
CPU Compatibility
| Socket | Compatible CPU Generation |
| LGA 1200 | Intel 10th Gen (Comet Lake) & Intel 11th (Rocket Lake) |
| LGA 1700 | Intel 12th Gen (Alder Lake) & Intel 13th Gen (Raptor Lake) |
Motherboard Compatibility
Both the LGA 1200 and LGA 1700 sockets are part of different chipsets.
LGA 1200 Supported Chipsets
| Intel 400 Series Chipsets | The Intel 400 Series includes motherboards like B460, H410, H470, and Z490 that natively support Intel’s 11th-generation processors. |
| Intel 300 Series Chipsets | This series of chipsets include the B365, H310, and H370. It natively supports the processors in Intel’s 10th generation line-up. |
| Intel 500 Series Chipset | Z590, H570, B560, and H510 are compatible with Intel 10th and 11th gen Intel CPUs. |
LGA 1700 Supported Chipsets
The LGA 1700 supported socket is normally found on Intel 600 and 700 Series chipsets.
| Intel 600 Series Chipsets | H610, B660, H670, Z690 (both 12 and 13th generation Intel CPUs) |
| Intel 700 Series Chipset | Z790 (Primarily made for Intel 13th generation processors. But is also backward compatible with 12th gen CPUs |
Overclocking Capabilities
When it comes to extracting more juice out of your CPU, the only way around is to overclock it. Both the LGA 1200 and LGA 1700 compatible CPUs are ideal for overclocking. But you’ll have to consider the right chipset that supports overclocking in this case.
As far as the LGA 1200 socket is concerned, it’s better to opt for chipsets like Z490 or Z590 to get the best out of overclocking. But even with the best chipsets with LGA 1200 on them, you cannot break the 5.0 GHz speed barrier.
The LGA 1700 socket breaks the traditional 5.0 GHz barrier, allowing you to overclock most 13th Intel CPUs over 5.2 GHz. For the best overclocking results, opt for chipsets like Z690 or Z790. So, the LGA 1700 socket gives you more headroom to enjoy higher clock speeds as compared to LGA 1200 socket.
Pros and Cons
Well, every newest generation LGA socket brings some sort of improvements over the previous generation socket. With LGA 1200 socket, you are able to build a PC around cheaper parts. The A motherboard that comes with LGA 1200 is cheaper to get.
At the same time, the older LGA 1200 limits you in terms of overclocking capabilities if you are a die-hard fan of overclocking. Moreover, there’s no support for the latest DDR5 memory modules in LGA 1200 compatible chipsets.
Going with an LGA 1700 socket chipset puts you at the front of any previous-generation chipsets. The LGA 1700 socket chipsets support both the DDR4 and DDR5 modules, so there’s a lot of freedom to build your PC around new and old memory modules.
Moreover, there’s a huge overclocking potential that comes with the LGA 1700 chipsets. In terms of cons, the LGA 1700-supported chipsets are expensive and they require modern cooling solutions.
Conclusion: Which is Better LGA 1200 or LGA 1700
Well, if we had to choose between these two, then it would be the LGA 1700. Moving up from the LGA 1200 to LGA 1700 brings loads of performance to your desk. Not only does LGA 1700 support DDR4 and DDR5 memory, but it also lets you stretch the wings of your 12th or 13th gen Intel processor to higher limits.
Although it requires you to have a new CPU cooler and invest a few more $$ in buying a relevant chipset, we believe that the LGA 1700 gives you the most bang for your investment. LGA 1200 on the side is cheaper, but it also limits you to stay away from modern techs like DDR5 and PCIe 5.0.

Hi, my name is Masab, a die-hard PC enthusiast and founder of this blog. I love to share my prior experience with computers on this blog. Ask me anything about building a PC or troubleshooting PC errors, I’m here to help.